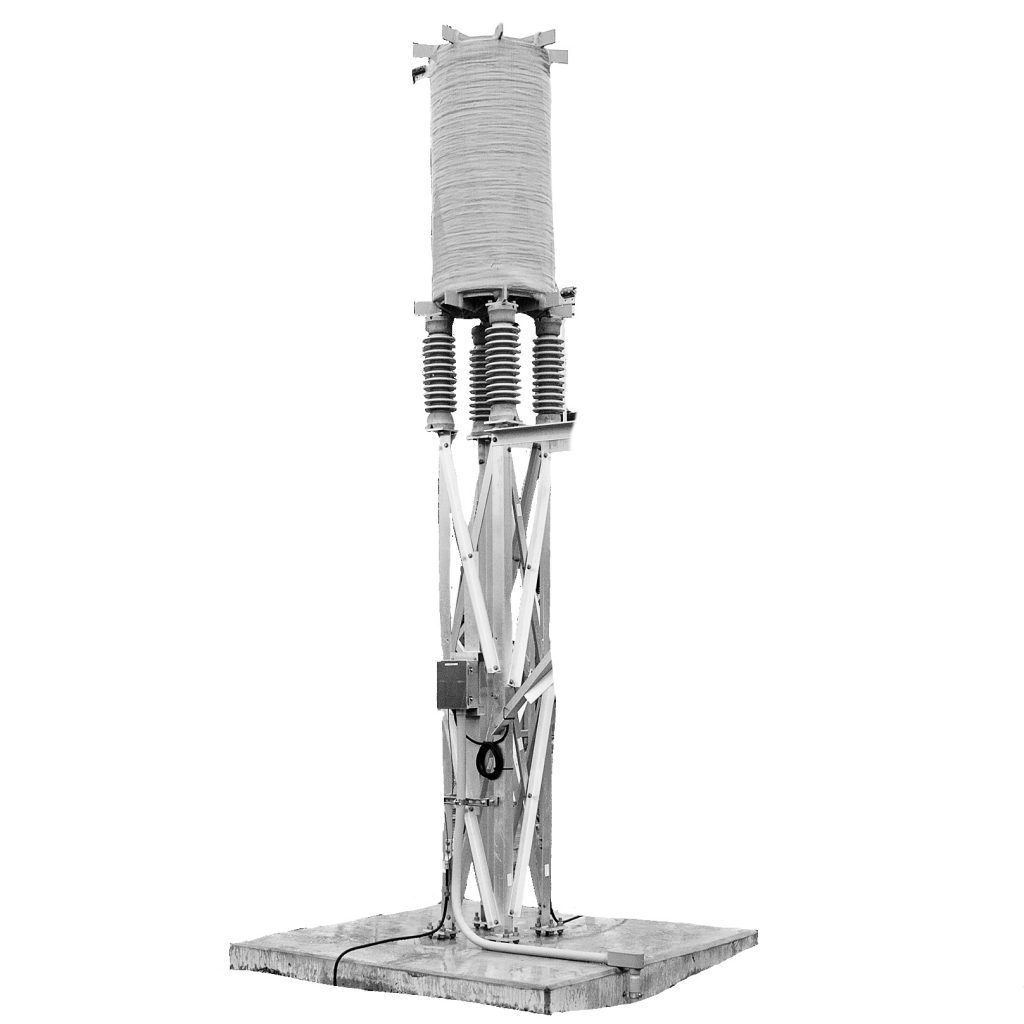

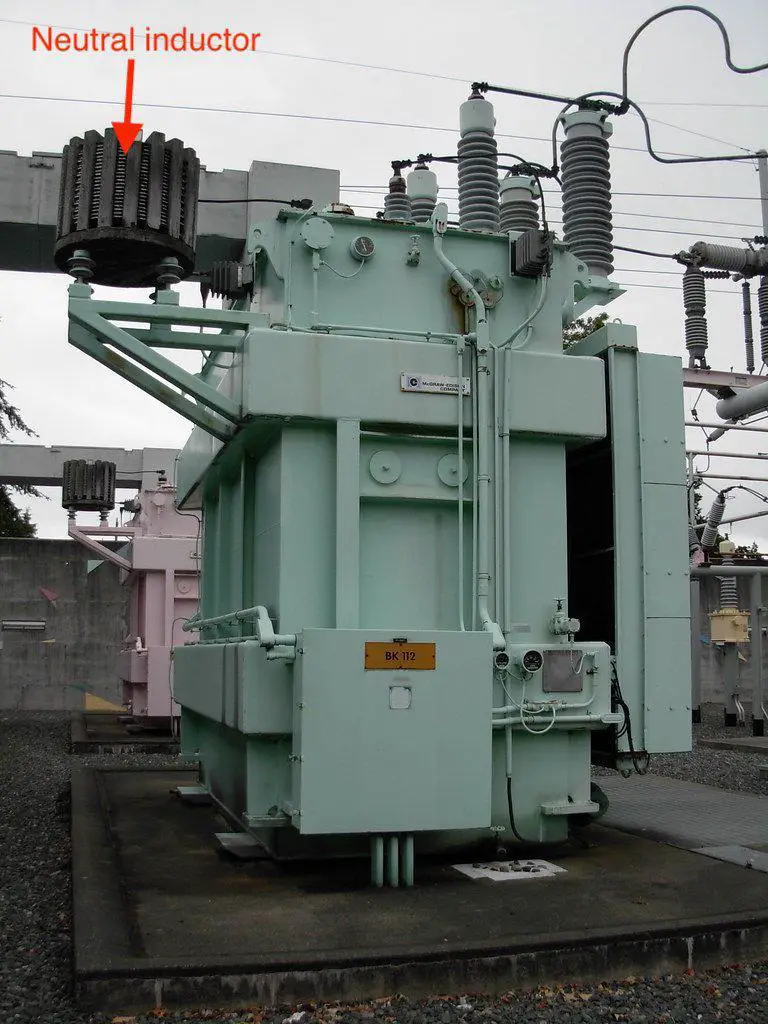
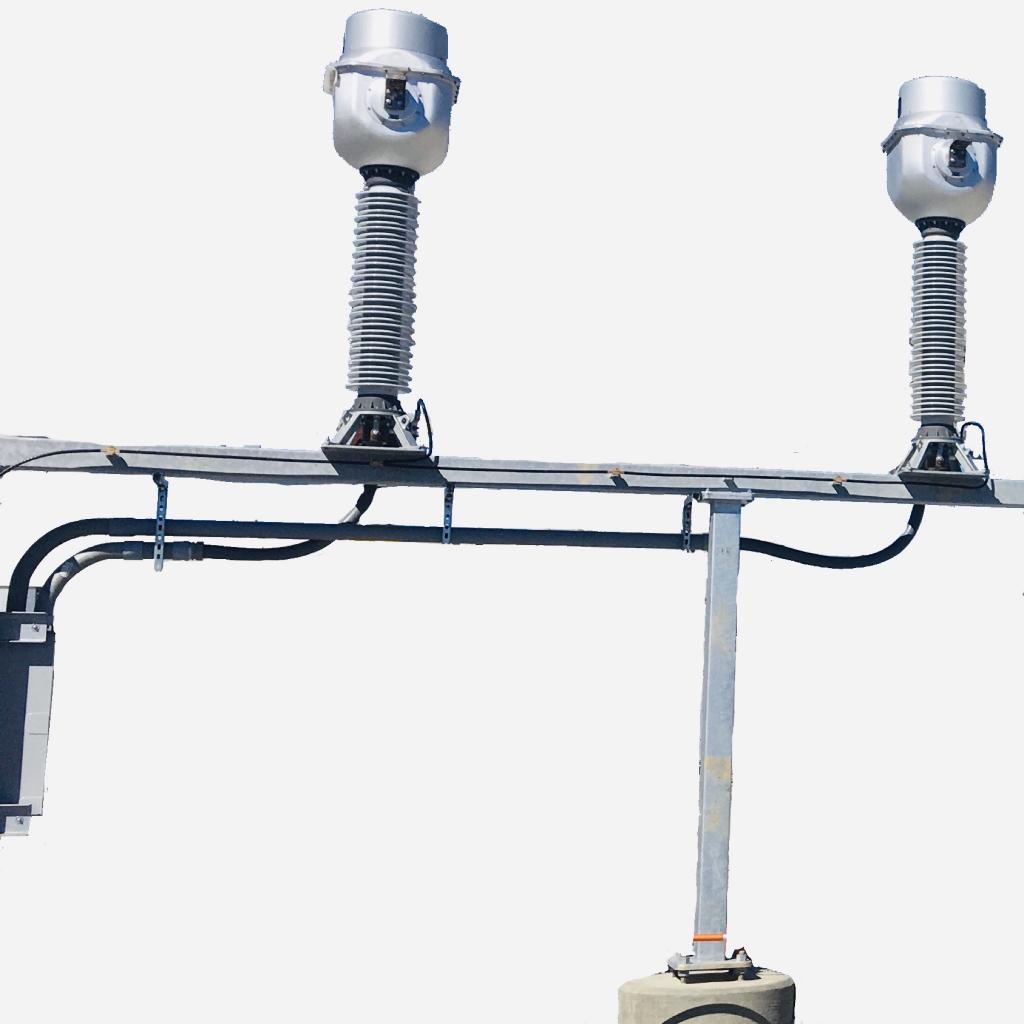
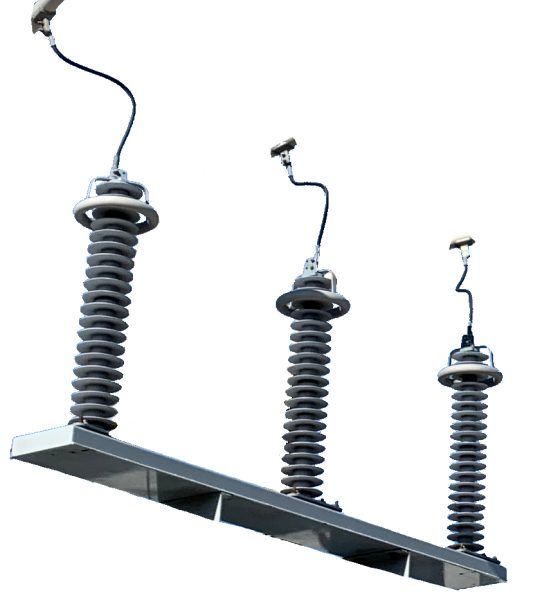
Purpose of inductor
An inductor prevents sudden change in current magnitude. It is installed in substations to:
- Limit
ground fault current entering the power system through transformer neutral. Read more.
- Limit in-rush currents associated with the energization of capacitor banks.
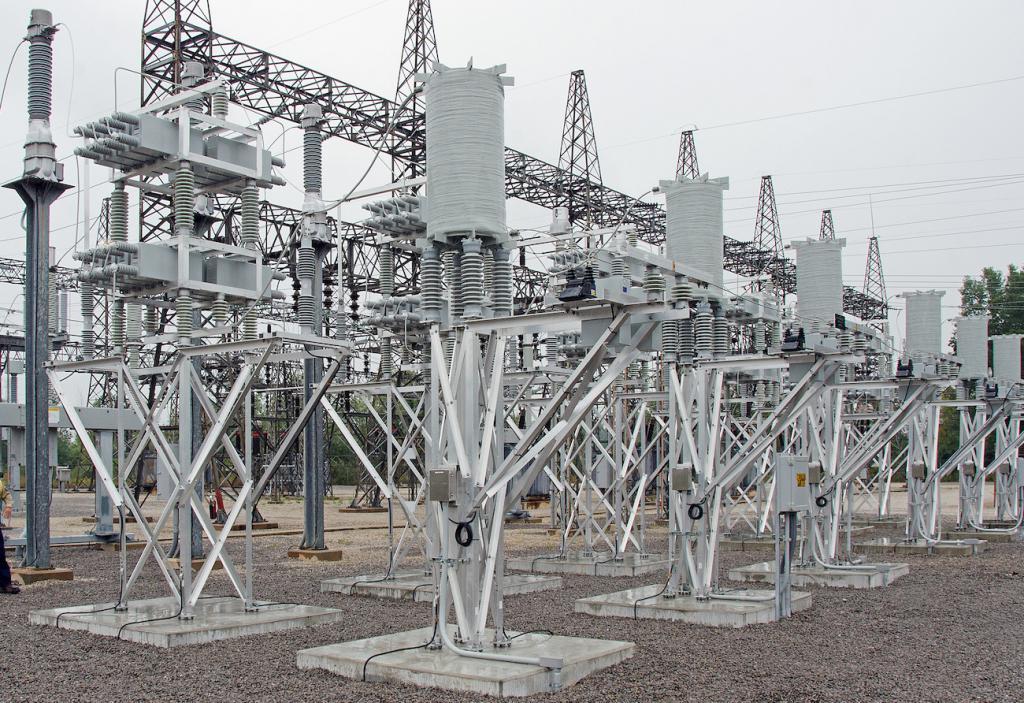

- Limit all variations of fault current 3-ph, L-G, L-L-G, etc. when tied in series on a line.
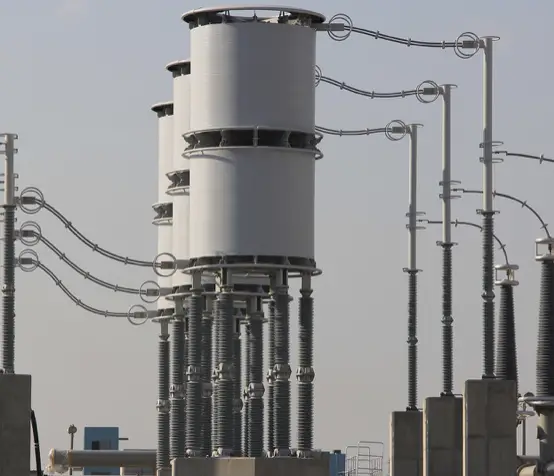
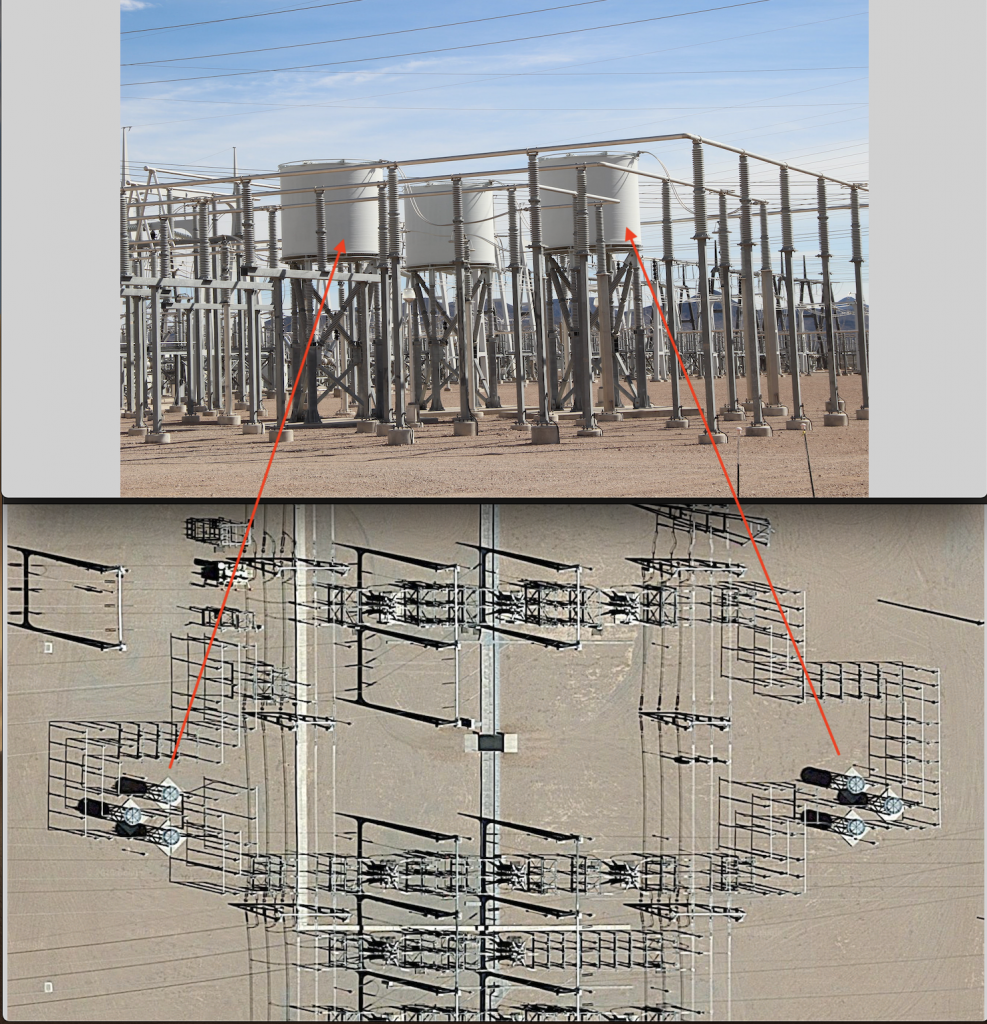


- On extremely long EHV transmission lines, the Ferranti effect is prominent. An inductor tapped off the t-line negates this effect (the leading vars generated on the long line is consumed by a shunt inductor.)
- Filter out harmonics (when used in conjunction with capacitor and resistor). Inductors are also implemented on other Flexible AC Transmission devices.
Cost of inductor:
- 15kV 800A neutral air core inductor (1 unit): ~$5,000
- 15kV 450A series air core inductor (3 units): ~$15,000
- 34kV 1000A series air core inductor (3 units): ~$60,000
- 138kV 600A series air core inductor (3 units): ~$60,000
- 345kV 120,000KVAR shunt air core inductor (3 units): ~$150,000
Lead time to procure inductor:
- ~20 weeks for medium voltage units
- ~30 weeks for HV & EHV units
Information on cost and lead time is for your general knowledge only. Contact vendor with your equipment specifications for actual figures.









This training and quiz was a true gem to find..brilliant!
Cannot typically find for free so thank you!
Wish there were more like it!